How Do I Know Whether I Have Nail Fungus?
Nail Fungus (Onychomycosis): How to Determine if You Have a Fungal Infection
Comparing the Modified Test Strip Diafactory Tinea Unguium with Traditional Laboratory Microbiology Tests
Overview
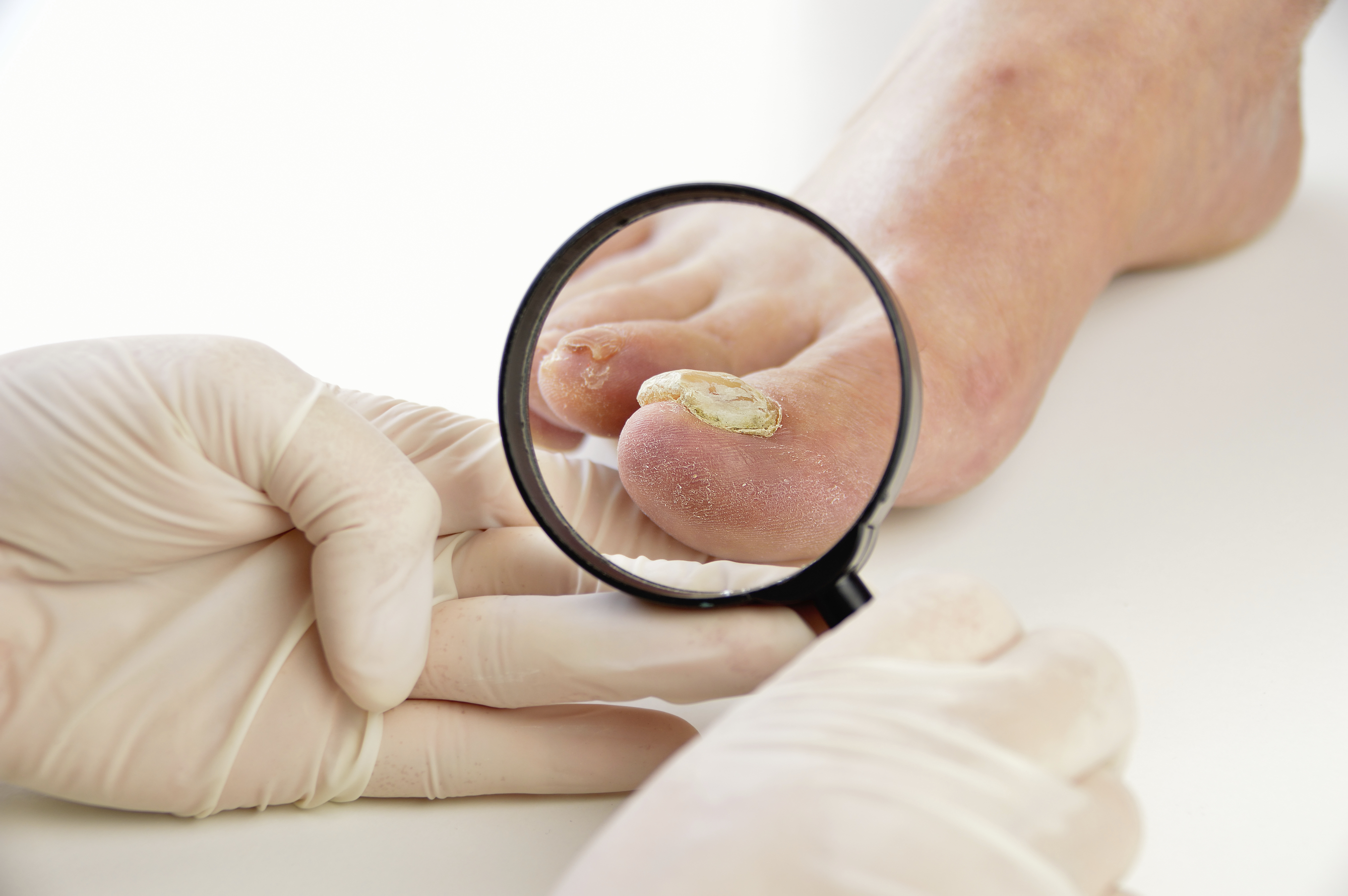
Nail fungus, also known as onychomycosis, is a common condition that can cause nails to become discolored, thickened, and brittle. It often starts as a small white or yellow spot under the tip of the nail but can spread deeper into the nail if left untreated, leading to more significant symptoms and complications.
Identifying whether your nail changes are due to a fungal infection is crucial for appropriate treatment. Several diagnostic methods exist, each with its advantages and limitations. This article reviews common diagnostic approaches, focusing on the modified test strip Diafactory Tinea Unguium and traditional laboratory microbiology tests.
Symptoms of Nail Fungus
Recognizing the symptoms of nail fungus is the first step toward diagnosis. Common signs include:
- Discoloration: Nails may turn white, yellow, brown, or even black.
- Thickened Nails: The nail may become thicker and harder to cut.
- Brittle or Crumbly Nails: Affected nails may become weak and prone to breaking.
- Nail Separation: The nail may detach from the nail bed, a condition known as onycholysis.
- Odor: In some cases, an unpleasant smell may accompany the infection.
While these symptoms suggest a fungal infection, they can also occur with other nail conditions, making accurate diagnosis essential.
Diagnostic Approaches
1. Traditional Laboratory Microbiology Tests
Laboratory tests have long been the gold standard for diagnosing onychomycosis. These tests typically involve collecting a sample of the affected nail for analysis. The most common laboratory methods include:
- Microscopy: The nail sample is examined under a microscope for the presence of fungal hyphae, the branching structures of the fungus.
- Culture: The sample is placed in a culture medium to grow any fungi present, which allows for precise identification.
- Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR): This molecular technique amplifies fungal DNA from the nail sample, offering highly sensitive detection of fungal species.
Advantages:
- Accuracy: Laboratory tests provide a definitive diagnosis, especially when microscopy and culture are combined.
- dentification of Fungal Species: Lab tests can identify the specific type of fungus, which is crucial for selecting the most effective treatment.
Disadvantages:
- Time: Results may take several days to weeks.
- Cost: These tests can be expensive, particularly if advanced methods like PCR are used.
- Sample Quality Dependence: The accuracy of the diagnosis depends on the quality and size of the nail sample taken.
2. Modified Test Strip Diafactory Tinea Unguium
The Diafactory Tinea Unguium test is a point-of-care diagnostic tool designed for rapid detection of fungal nail infections. It involves placing a small sample of the affected nail on a test strip, which reacts to the presence of fungal elements, providing results within minutes.
Advantages:
- Speed: Results are available within minutes, making it a convenient option in a clinical setting.
- Cost-Effectiveness: This test is generally less expensive than traditional laboratory tests.
- Ease of Use: The test can be conducted in a clinic without the need for specialized equipment.
Disadvantages:
- Lower Specificity: While effective at detecting the presence of a fungal infection, the test may not identify the specific fungal species involved.
- Sensitivity: There is a slight risk of false negatives, meaning the test might not detect all cases of fungal infection.
Comparative Efficacy
A study published in Mycoses (2023) reported that while the Diafactory test is convenient and quick, it has a slightly lower sensitivity (around 85%) compared to traditional laboratory methods, which show around 95% sensitivity. Another study from the Journal of Fungi (2024) supported the use of PCR for confirmatory testing due to its higher diagnostic accuracy, especially in persistent or complicated cases. Which Test Should You Choose? The choice between the Diafactory Tinea Unguium test and traditional laboratory methods depends on the patient’s needs. For a quick and affordable diagnosis, the Diafactory test is a good option. However, for more severe or recurring infections, traditional lab tests are recommended for their higher accuracy and specificity
Which Test Should You Choose?
The choice between the Diafactory Tinea Unguium test and traditional laboratory microbiology tests depends on the specific needs of the patient. For individuals seeking a quick and affordable diagnosis, the Diafactory test is a viable option. However, for patients with severe, persistent, or recurrent infections, traditional laboratory tests offer more detailed information that can guide more effective treatment strategies.
Conclusion
Diagnosing a fungal nail infection requires a careful balance between speed, cost, and accuracy. While the Diafactory Tinea Unguium test provides a rapid and cost-effective method for detecting onychomycosis, traditional laboratory tests remain the gold standard for confirming the diagnosis and identifying the specific fungal species involved. Consulting with a healthcare provider is essential for selecting the most appropriate diagnostic method and ensuring optimal treatment outcomes.
References
1. Tsunemi, Y., et al. (2023). “Comparative Sensitivity and Specificity of Diafactory Tinea Unguium vs. Traditional Laboratory Methods in Diagnosing Onychomycosis.” Mycoses, 66(2), 145-152. 2.
2. Gupta, A. K., et al. (2024). “Clinical Diagnosis and Laboratory Testing of Abnormal Appearing Toenails: A Retrospective Assessment of Confirmatory Testing for Onychomycosis in the United States.” Journal of Fungi, 10(2), 149. DOI: 10.3390/jof10020149.
